Abdera, Thrace on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Abdera () is a
 The
The  Abdera had flourished especially in ancient times mainly for two reasons: because of the large area of their territory and their highly strategic position. The city controlled two great road passages (one of Nestos river and other through the mountains north of Xanthi). Furthermore, from their ports passed the sea road, which from Troas led to the Thracian and then the Macedonian coast.
The ruins of the town may still be seen on Cape Balastra (40°56'1.02"N 24°58'21.81"E); they cover seven small hills, and extend from an eastern to a western harbor; on the southwestern hills are the remains of the medieval settlement of Polystylon.
Abdera had flourished especially in ancient times mainly for two reasons: because of the large area of their territory and their highly strategic position. The city controlled two great road passages (one of Nestos river and other through the mountains north of Xanthi). Furthermore, from their ports passed the sea road, which from Troas led to the Thracian and then the Macedonian coast.
The ruins of the town may still be seen on Cape Balastra (40°56'1.02"N 24°58'21.81"E); they cover seven small hills, and extend from an eastern to a western harbor; on the southwestern hills are the remains of the medieval settlement of Polystylon.
municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
in the Xanthi regional unit of Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to t ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
. In classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
, it was a major Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''polis
''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Later, it also ...
'' on the Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
coast.
The ancient polis is to be distinguished from the municipality, which was named in its honor. The polis lay 17 km east-northeast of the mouth of the Nestos River
Nestos ( ), Mesta ( ), or formerly the Mesta Karasu in Turkish (Karasu meaning "black river"), is a river in Bulgaria and Greece. It rises in the Rila Mountains and flows into the Aegean Sea near the island of Thasos. It plunges down towering c ...
, almost directly opposite the island of Thasos
Thasos or Thassos ( el, Θάσος, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate re ...
. It was a colony placed in previously unsettled Thracian territory, not then a part of Hellas, during the age of Greek colonization
Greek colonization was an organised colonial expansion by the Archaic Greeks into the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea in the period of the 8th–6th centuries BC.
This colonization differed from the migrations of the Greek Dark Ages in that i ...
. The city that developed from it became of major importance in ancient Greece. After the 4th centuryAD it declined, contracted to its acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens, ...
, and was abandoned, never to be reoccupied except by archaeologists.
Meanwhile, life went on as the changing population settled in other communities in the region. One named Polystylus changed its name to Abdera. In 2011 the municipality of Abdera was synoecized from three previous municipalities comprising a number of modern settlements. The ancient site remains in it as a ruin. The municipality of Abdera has 19,005 inhabitants (2011). The seat of the municipality is the town Genisea
Genisea ( el, Γενισέα) is a town in the Vistonida municipal unit, within the municipality of Abdera in the Xanthi regional unit of Greece. It is the seat of the municipality Abdera. According to the 2011 census, the population of Genisea ...
.
Name
The name ''Abdera'' is of Phoenician origin and was shared in antiquity byAbdera, Spain
__NOTOC__
Abdera was an ancient Carthaginian and Roman port on a hill above the modern Adra on the southeastern Mediterranean coast of Spain. It was located between Malaca (now Málaga) and Carthago Nova (now Cartagena) in the district inhabite ...
and a town near Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classi ...
in North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
. It was variously Hellenized
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in th ...
as (''Ábdēra''), (''Aúdēra''), (''Ábdara''), (''Ábdēron''), and (''Ábdēros''), before being Latinized as ''Abdera''. Greek legend attributed the name to an eponymous Abderus
In Greek mythology, Abderus or Abderos (Ancient Greek: Ἄβδηρος) was a divine hero, reputed by some to be one of Heracles' lovers ( eromenoi), and reputedly a son of Hermes by some accounts, and eponym of Abdera, Thrace. Pseudo-Scymnos, ''Ci ...
who fell nearby and was memorialized by Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted the Gr ...
's founding of a city at the location.
The present-day town is written Avdira () and pronounced in modern Greek
Modern Greek (, , or , ''Kiní Neoellinikí Glóssa''), generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek (, ), refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the ...
.
History
Antiquity

 The
The Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
ns apparently began the settlement of Abdera at some point before the mid-7th century and the town long maintained Phoenician standards in its coinage.
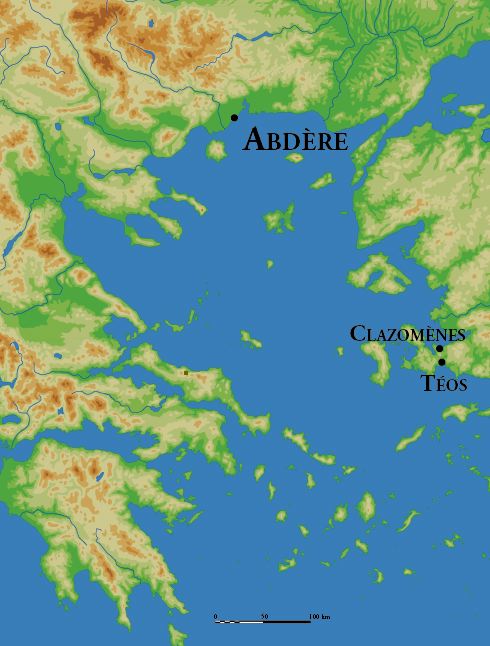
The Greek settlement was begun as a failed colony from Klazomenai
Klazomenai ( grc, Κλαζομεναί) or Clazomenae was an ancient Greek city on the coast of Ionia and a member of the Ionian League. It was one of the first cities to issue silver coinage. Its ruins are now located in the modern town Urla n ...
, traditionally dated to 654BC. (Evidence in 7th-century-BC Greek pottery
Ancient Greek pottery, due to its relative durability, comprises a large part of the archaeological record of ancient Greece, and since there is so much of it (over 100,000 painted vases are recorded in the Corpus vasorum antiquorum), it has exe ...
tends to support the traditional date but the exact timing remains uncertain.) Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known f ...
reports that the leader of the colony had been Timesios but, within his generation, the Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. ...
had expelled the colonists. Timesios was subsequently honored as a local protective spirit by the later Abderans from Teos. Others recount various legends about this colony. Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''P ...
and Aelian relate that Timesios grew insufferable to his colonists because of his desire to do everything by himself; when one of their children let him know how they all really felt, he quit the settlement in disgust; modern scholars have tried to split the difference between the two accounts of early Abdera's failure by giving the latter as the reason for Timesios's having left Klazomenai.
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
describes Abdera as "a Thracian city" at the time of Anacreon
Anacreon (; grc-gre, Ἀνακρέων ὁ Τήϊος; BC) was a Greek lyric poet, notable for his drinking songs and erotic poems. Later Greeks included him in the canonical list of Nine Lyric Poets. Anacreon wrote all of his poetry in the ...
and the migration of people from Teos
Teos ( grc, Τέως) or Teo was an ancient Greek city on the coast of Ionia, on a peninsula between Chytrium and Myonnesus. It was founded by Minyans from Orchomenus, Ionians and Boeotians, but the date of its foundation is unknown. Teos was ...
to that area. The successful colonisation occurred in 544BC, when the majority of the people of Teos
Teos ( grc, Τέως) or Teo was an ancient Greek city on the coast of Ionia, on a peninsula between Chytrium and Myonnesus. It was founded by Minyans from Orchomenus, Ionians and Boeotians, but the date of its foundation is unknown. Teos was ...
(including the poet Anacreon
Anacreon (; grc-gre, Ἀνακρέων ὁ Τήϊος; BC) was a Greek lyric poet, notable for his drinking songs and erotic poems. Later Greeks included him in the canonical list of Nine Lyric Poets. Anacreon wrote all of his poetry in the ...
) migrated to Abdera to escape the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
yoke. The chief coin type, a '' griffon'', is identical with that of Teos; the rich silver coinage is noted for the beauty and variety of its reverse types. Endnotes:
*''Mittheil. d. deutsch. Inst. Athens'', xii. (1887), p. 161 (Regel);
*''Mém. de l'Acad. des Inscriptions'', xxxix. 211;
*K. F. Hermann, ''Ges. Abh.'' 90-111, 370 ff.
In 513 and 512BC, the Persians, under Darius conquered Abdera, by which time the city seems to have become a place of considerable importance, and is mentioned as one of the cities which had the expensive honour of entertaining the great king on his march into Greece. In 492BC, after the Ionian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisf ...
, the Persians again conquered Abdera, again under Darius I
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his ...
but led by his general Mardonius. On his flight after the Battle of Salamis
The Battle of Salamis ( ) was a naval battle fought between an alliance of Greek city-states under Themistocles and the Persian Empire under King Xerxes in 480 BC. It resulted in a decisive victory for the outnumbered Greeks. The battle was ...
, Xerxes stopped at Abdera and acknowledged the hospitality of its inhabitants by presenting them with a tiara and scimitar of gold. Thucydides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of "scientifi ...
mentions Abdera as the westernmost limit of the Odrysian kingdom
The Odrysian Kingdom (; Ancient Greek: ) was a state grouping many Thracian tribes united by the Odrysae, which arose in the early 5th century BC and existed at least until the late 1st century BC. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria an ...
when at its height at the beginning of the Peloponnesian war
The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of th ...
. It later became part of the Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pl ...
and fought on the side of Athens in the Peloponnesian war.
Abdera was a wealthy city, the third richest in the League, due to its status as a prime port for trade with the interior of Thrace and the Odrysian kingdom
The Odrysian Kingdom (; Ancient Greek: ) was a state grouping many Thracian tribes united by the Odrysae, which arose in the early 5th century BC and existed at least until the late 1st century BC. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria an ...
. In 408BC, Abdera was reduced under the power of Athens by Thrasybulus
Thrasybulus (; grc-gre, Θρασύβουλος ; 440 – 388 BC) was an Athenian general and democratic leader. In 411 BC, in the wake of an oligarchic coup at Athens, the pro-democracy sailors at Samos elected him as a general, making him a ...
, then one of the Athenian generals in that quarter.
A valuable prize, the city was repeatedly sacked: by the Triballi
The Triballi ( grc, Τριβαλλοί, Triballoí, lat, Triballi) were an ancient people who lived in northern Bulgaria in the region of Roman Oescus up to southeastern Serbia, possibly near the territory of the Morava Valley in the late Iron A ...
in 376BC, Philip II of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king ('' basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ...
in 350BC; later by Lysimachos of Thrace, the Seleucids
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
, the Ptolemies, and again by the Macedonians. In 170BC the Roman armies and those of Eumenes II of Pergamon besieged and sacked it.
The town seems to have declined in importance after the middle of the 4th centuryBC. Cicero ridicules the city as a byword for stupidity in his letters to Atticus, writing of a debate in the Senate, "Here was Abdera, but I wasn't silent" ("Hic, Abdera non tacente me"). Nevertheless, the city counted among its citizens the philosophers Democritus
Democritus (; el, Δημόκριτος, ''Dēmókritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; – ) was an Ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an atomic theory of the universe. No ...
, Protagoras
Protagoras (; el, Πρωταγόρας; )Guthrie, p. 262–263. was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher and rhetorical theorist. He is numbered as one of the sophists by Plato. In his dialogue '' Protagoras'', Plato credits him with inventing the r ...
and Anaxarchus
Anaxarchus (; grc, Ἀνάξαρχος; ) was a Greek philosopher of the school of Democritus. Together with Pyrrho, he accompanied Alexander the Great into Asia. The reports of his philosophical views suggest that he was a forerunner of Pyrrhon ...
, historian and philosopher Hecataeus of Abdera :''See Hecataeus of Miletus for the earlier historian.''
Hecataeus of Abdera or of Teos ( el, Ἑκαταῖος ὁ Ἀβδηρίτης), was a Greek historian and Pyrrhonist philosopher who flourished in the 4th century BC.
Life
Diogenes La ...
, and the lyric poet Anacreon
Anacreon (; grc-gre, Ἀνακρέων ὁ Τήϊος; BC) was a Greek lyric poet, notable for his drinking songs and erotic poems. Later Greeks included him in the canonical list of Nine Lyric Poets. Anacreon wrote all of his poetry in the ...
. Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' ...
speaks of Abdera as being in his time a free city.
 Abdera had flourished especially in ancient times mainly for two reasons: because of the large area of their territory and their highly strategic position. The city controlled two great road passages (one of Nestos river and other through the mountains north of Xanthi). Furthermore, from their ports passed the sea road, which from Troas led to the Thracian and then the Macedonian coast.
The ruins of the town may still be seen on Cape Balastra (40°56'1.02"N 24°58'21.81"E); they cover seven small hills, and extend from an eastern to a western harbor; on the southwestern hills are the remains of the medieval settlement of Polystylon.
Abdera had flourished especially in ancient times mainly for two reasons: because of the large area of their territory and their highly strategic position. The city controlled two great road passages (one of Nestos river and other through the mountains north of Xanthi). Furthermore, from their ports passed the sea road, which from Troas led to the Thracian and then the Macedonian coast.
The ruins of the town may still be seen on Cape Balastra (40°56'1.02"N 24°58'21.81"E); they cover seven small hills, and extend from an eastern to a western harbor; on the southwestern hills are the remains of the medieval settlement of Polystylon.
Modern
Avdira as a modern administrative unit (community) was established in 1924, and consisted of the villages Avdira, Myrodato (Kalfalar), Pezoula, Giona, Veloni andMandra
Mandra ( el, Μάνδρα), is a town and former municipality in West Attica, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Mandra-Eidyllia, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an ...
, but Myrodato and Mandra became separate communities in 1928. The municipality Avdira was formed in 1997 by the merger of the former communities Avdira, Mandra, Myrodato and Nea Kessani. At the 2011 local government reform it merged with the former municipalities Selero
Selero ( el, Σέλερο; tr, Gökçeler) is a village and a former community in the Xanthi regional unit, East Macedonia and Thrace, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. ...
and Vistonida
Vistonida ( el, Βιστωνίδα) is a former municipality in the Xanthi regional unit, East Macedonia and Thrace, Greece. It was named after Lake Vistonida. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Abdera, of whic ...
, and the town Genisea
Genisea ( el, Γενισέα) is a town in the Vistonida municipal unit, within the municipality of Abdera in the Xanthi regional unit of Greece. It is the seat of the municipality Abdera. According to the 2011 census, the population of Genisea ...
became its seat.
The municipality has an area of 352.047 km2, the municipal unit 161.958 km2. The municipal unit Avdira is subdivided into the communities Avdira, Mandra, Myrodato and Nea Kessani. The community Avdira consists of the settlements Avdira, Giona, Lefkippos, Pezoula and Skala.
Landmarks
Landmarks of Abdera include the Archaeological Museum of Abdera, and Agios Ioannis Beach (also ''Paralia Avdiron'') near the village Lefkippos.Famous people
*Democritus
Democritus (; el, Δημόκριτος, ''Dēmókritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; – ) was an Ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an atomic theory of the universe. No ...
* Protagoras
Protagoras (; el, Πρωταγόρας; )Guthrie, p. 262–263. was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher and rhetorical theorist. He is numbered as one of the sophists by Plato. In his dialogue '' Protagoras'', Plato credits him with inventing the r ...
* Hecateus
* Nicaenetus
See also
*List of ancient Greek cities
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby union ...
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
*External links
* * * . {{Authority control Municipalities of Eastern Macedonia and Thrace Populated places in Xanthi (regional unit) Ionian colonies in Thrace Ancient Greek cities Members of the Delian League Populated places established in the 7th century BC Greek city-states Populated places in ancient Thrace Phoenician colonies in Greece